Axminster
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
See weaving.
runner
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
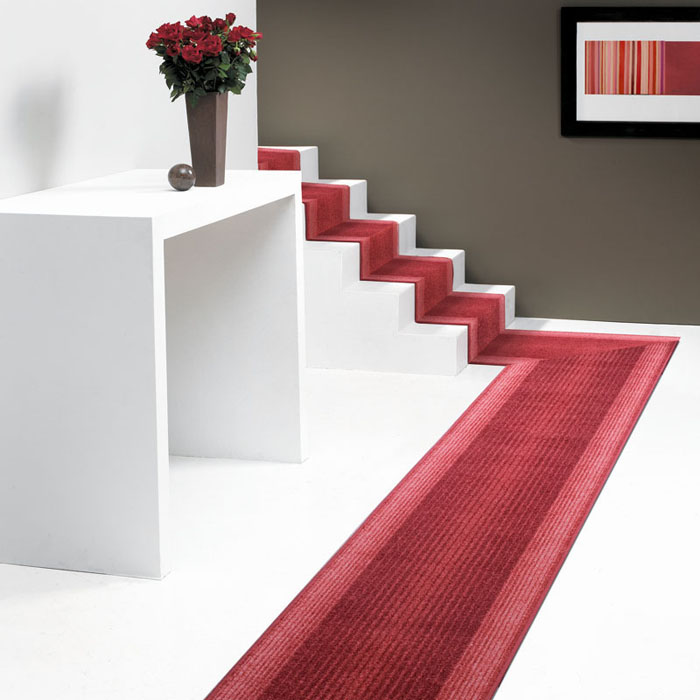

A narrow carpet lane used in the length covering a part of the width of a floor such as in corridors and on stairs.
Berber
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Berber is a distinctive loop pile carpet made of coarse spun yarns. The loops of a berber carpet are normally 10 to 20 mm high and contain highlight flecks formed by fibres of different colours. Berber carpets are also the traditional hand-woven carpets of the Berber people of North Africa, which use a distinct knot that gives a similar appearance to a modern Berber carpet. See also berber-look and loop pile.
berber-look (or Berber carpet style)
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

Berber-look is a term that is used to describe rustic, plain colour carpet having small flecks of darker colours on lighter shades of background colours. It is used to describe the traditional loop Berber carpet but also the look of cut pile carpet having the same visual effect. Berber-look carpet is generally made from wool but sometimes also from manmade fibre like polypropelene imitating wool. See also Berber.
bouclé
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

 This is a carpet with a loop pile. The loops are close to each other and have the same height. The loops are 5 to 10 mm high. This makes a very wear-resistant and durable carpet. It is accordingly also suitable for spaces with high traffic such as playrooms, kitchens, stairs, corridors and halls.
This is a carpet with a loop pile. The loops are close to each other and have the same height. The loops are 5 to 10 mm high. This makes a very wear-resistant and durable carpet. It is accordingly also suitable for spaces with high traffic such as playrooms, kitchens, stairs, corridors and halls.
frisé
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń


This is a carpet with a cut pile that is shorter than the Saxony but of highly twisted and fixed yarns (frisé yarn). This gives a tousled and lively structure without the tall pile height of the shag.
It is a carpet with a fanciful appearance that comes into its own in modern interiors. The tousled structure means the walking routes are less conspicuous so this carpet can also be used in spaces with high traffic.
It is also suitable for stairs, corridors and playrooms.
action back (synthetic jute)
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
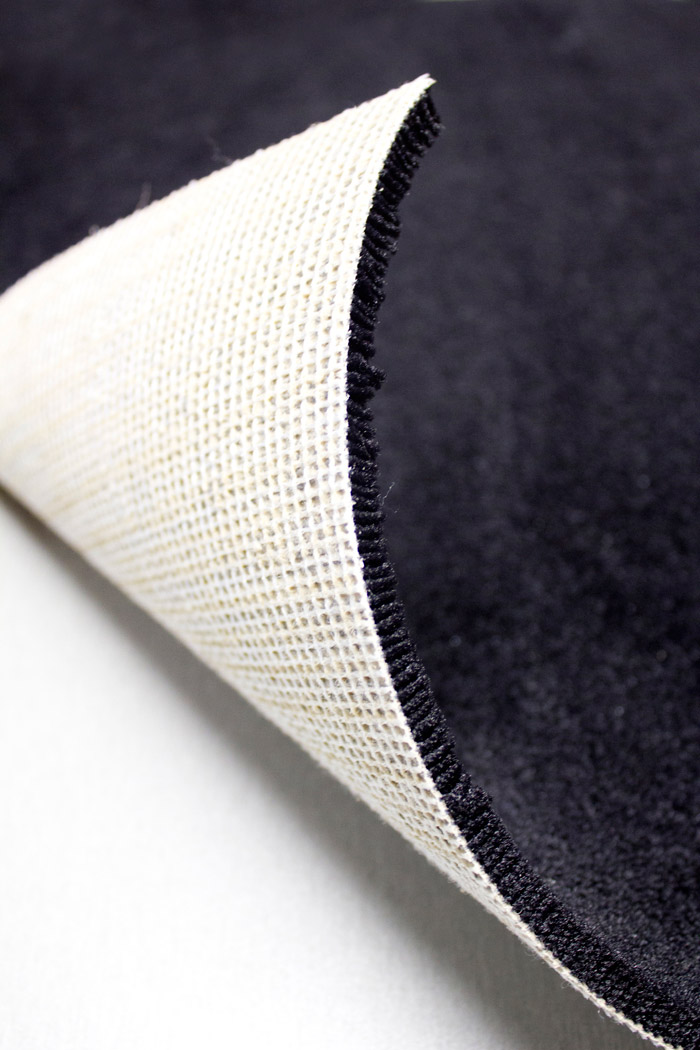

A gauze fabric that consists of a warp in PP tape yarn and a weft of PP spun yarn.
The name Actionbac® was initially a brand name of Amoco (now PROPEX). It is used as secondary backing for tufted carpets.
gel foam
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
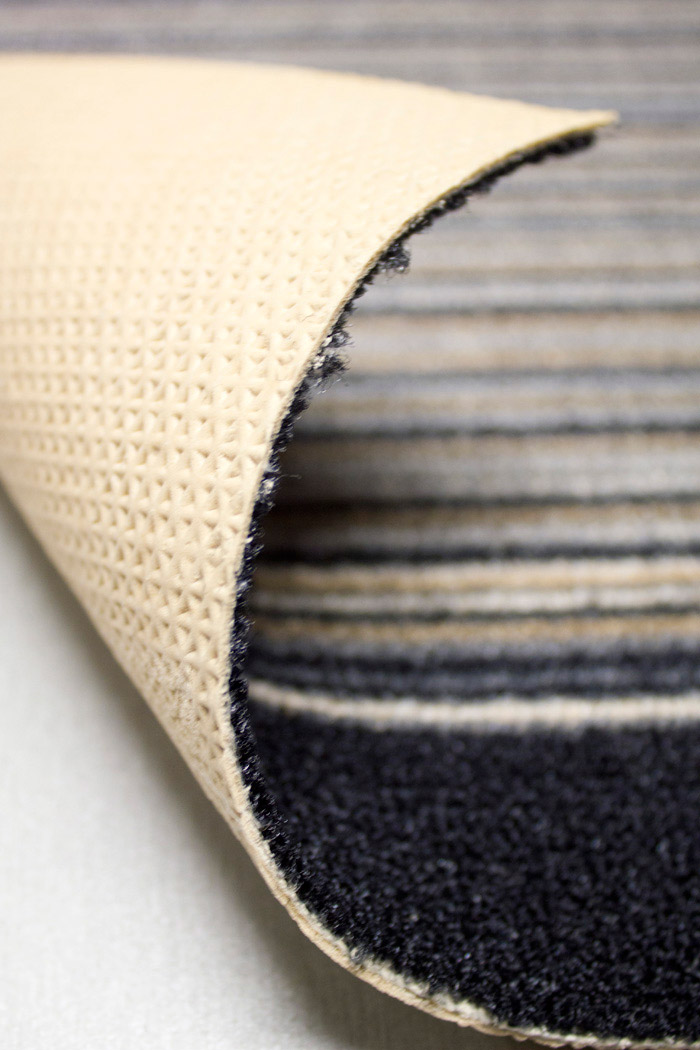
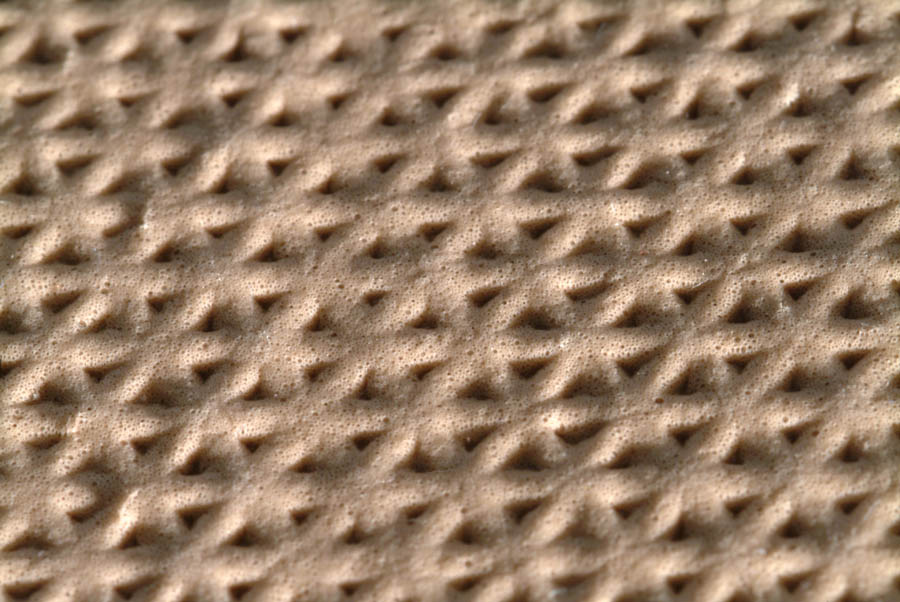


The gel foam is a type of foam backing applied as secondary backing to tufted carpets. Compared to foam backing gel foam has a better foam structure and it is insensitive to water. It is usually used as a backing of runner carpets. See also runner.
deep cleaning
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
A general term for carpet cleaning techniques where both the pile as well as the back of the carpet is cleaned. Some examples are: spray extraction and steam cleaning.
rug
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
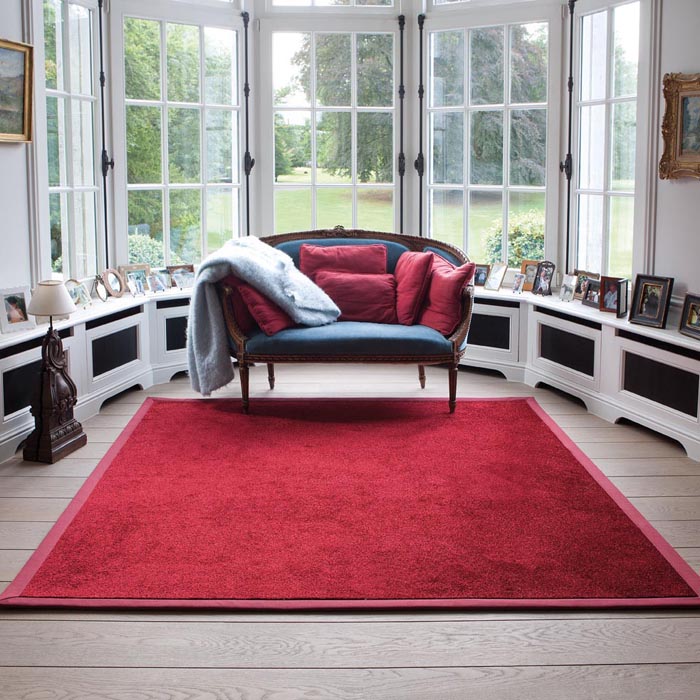

A carpet of a certain form with limited dimensions. Rugs are laid on top of other, usually harder floor coverings such as ceramic tiles or parquet floors.
wall-to-wall carpet
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
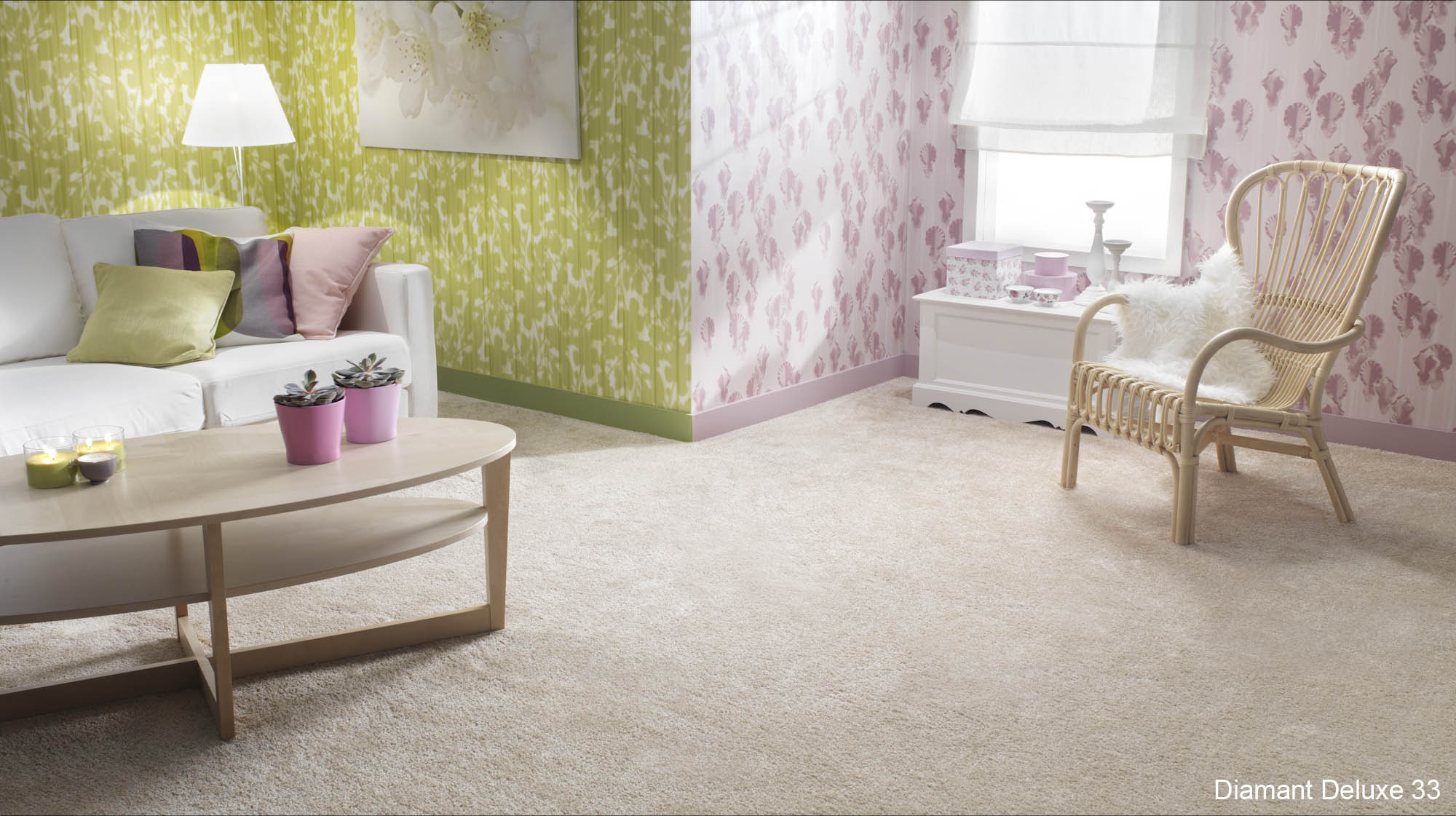

A carpet that covers the complete surface of a floor in a room. Normally the carpets are 4 or 5 m wide. In larger spaces a number of carpets are fitted side by side.
Nylon
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
See polyamide.
stain resistance treatment
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Treatment of the pile of the carpet to counteract staining of the carpet.
wear-resistance
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
The resistance of a carpet to wear. There are various tests to evaluate the wearing of a carpet. The results of these tests are used to decide upon use classification of a particular carpet. See also PRODIS.
anti-soil treatment
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
See soil resistance treatment.
foam back
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
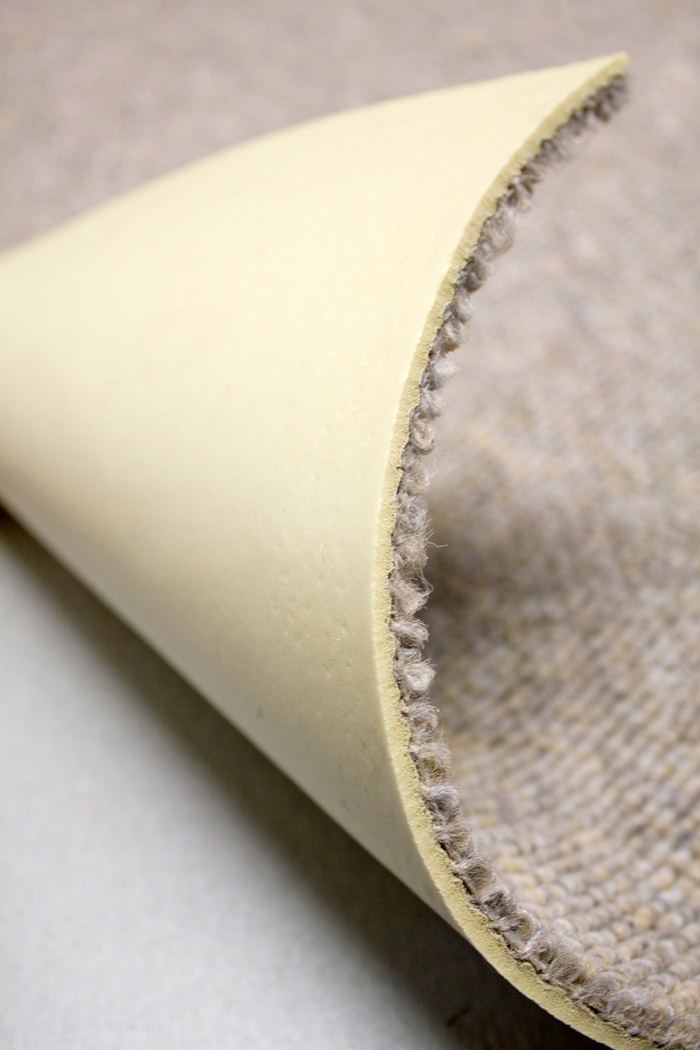

A foam back is secondary backing applied to the back of the carpet.
Foam backs provide a good feeling of comfort and good acoustic insulation. The thickness of the foam back evens the surface so no carpet underlay is needed.
The foam back is a compound with latex as the most important component.
backing
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
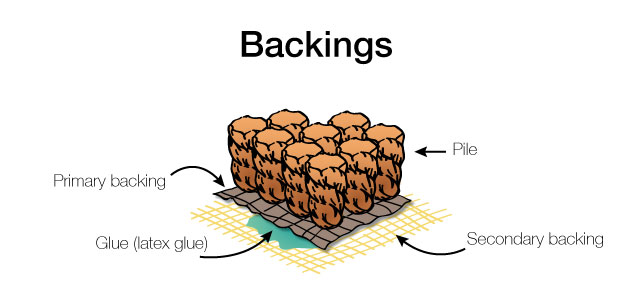
A general term to indicate the parts of the backing of a tufted carpet. A further distinction is made between the primary backing and the secondary backing. Primary backing is a fabric that is used when tufting to stitch in yarns. It forms the basis of a tufted carpet. The primary backing is usually a woven fabric or a nonwoven. Secondary backing is a second fabric or a polymer layer applied to the back of a tufted carpet.
carpet underlay
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

A carpet underlay is a layer of rubber or polyurethane or a felt layer placed between the carpet and the ground.
Use of an underlay reduces the friction of the carpet against a hard ground surface so the carpet wears less quickly and the feeling of comfort is increased.
polyester
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
A synthetic raw material from which textile fibres and yarns are manufactured.
Polyester fibres have good strength, elasticity and wear-resistance.
The wear-resistance is less than that of polyamide.
polyamide (Nylon)
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
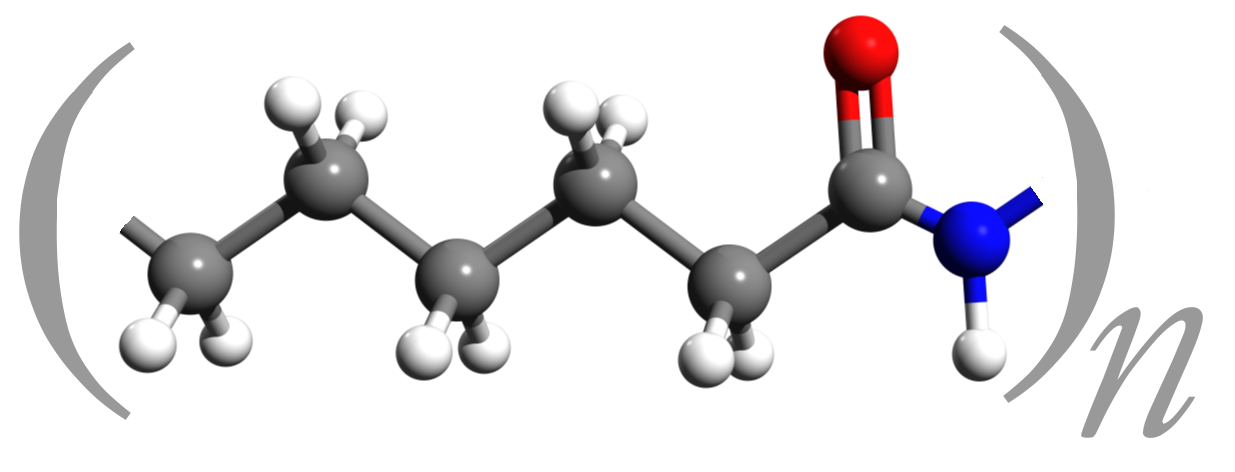
A synthetic raw material from which textile fibres and particularly carpet fibres are manufactured.
Polyamide distinguishes itself by good elasticity and excellent wear-resistance so it is a very good raw material for carpet yarn. Two types are used, being polyamide 6 and polyamide 6.6.
polypropene (polypropylene)
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
A synthetic raw material from which textile fibres and yarns are manufactured. Polypropene fibres have good strength but only moderate elasticity and are therefore less suitable for carpets subjected to intense traffic unless this characteristic is compensated by an appropriate (read: higher) pile density and/or a lower pile height. In heavy traffic areas loop pile carpets are alsoless vulnerable to crushing than cut pile carpets. Polypropene is also known by the older name polypropylene. This last name is still the most common name among producers and consumers.
natural fibre
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Natural fibres are textile fibres occurring in the natural environment.
They originate from plants such as cotton, jute and sisal or from animals such as the wool from the fleece of sheep.
PRODIS
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
PRODIS is a comprehensive consumer information system that integrates information on environmental issues, consumer health and safety topics as well as information on use areas and additional characteristics of textile floorcoverings.
More information about PRODIS can be found
here.
resilience
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
The ability of a carpet to return to its original thickness after static or dynamic loading (compression).
The higher the resilience, the less quickly walking paths are visible in the carpet. Carpets with higher resilience are more durable than carpets with lower resilience.
Resilience is closely associated with the raw material from which the pile is manufactured. Polyamide has the best resilience.
Saxony
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

 This is a carpet with a cut pile. The pile consists of thicker twisted and fixed yarns. The ends of the piles are clearly distinguishable from each other (pinpoint effect) so the carpet has a grainy appearance. The pile height is usually limited to 20 mm. A Saxony is a stylish carpet popular in traditional and formal spaces. It is sensitive to walking routes and therefore suitable for spaces with low traffic such as bedrooms, living rooms and dining rooms.
This is a carpet with a cut pile. The pile consists of thicker twisted and fixed yarns. The ends of the piles are clearly distinguishable from each other (pinpoint effect) so the carpet has a grainy appearance. The pile height is usually limited to 20 mm. A Saxony is a stylish carpet popular in traditional and formal spaces. It is sensitive to walking routes and therefore suitable for spaces with low traffic such as bedrooms, living rooms and dining rooms.
scroll
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Scroll is a tufting technique used to tuft high-pile and low-pile carpets according to a certain pattern.
Carpets manufactured with this technique are often called scrolls especially when they are tip-sheared. See also tip-sheared.
shag
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń



This is a carpet with a cut pile and a very tall pile height of approx 40 mm. There are even supershags with a pile height of 70 mm. Because of the tall pile height the pile yarns can no longer remain upright, so they fall and an entangled surface originates that resembles fine cut tobacco (shag).
It is a very soft and decorative carpet but with little wear-resistance. It is particularly suitable for informal spaces with low traffic. It is unsuitable for stairs.
loop pile
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

A term to refer to carpets with a loop pile. The term is also used to refer to the technique and machines used to produce carpets with a loop pile.
soil resistance treatment
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

Treatment of the pile of the carpet to counteract soiling of the carpet. In most cases water- and/or oil-repellent products are applied.
shading
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
A visible colour difference (darker or lighter) that occurs in carpets with a cut pile. The colour difference is caused by a difference in direction in which the light that falls on the carpet is reflected because fibres are bent in different directions.
When using glossy yarns this same fysical light-distortion-effect is even accentuated and gives these carpets their specific and unique glossy character.
tip-sheared
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń

A carpet with a loop pile of different pile heights with the tips of the highest piles being slightly torn open. This gives a special effect of partly cut/not cut high pile and loop pile. See also scroll.
cut pile
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń


A term to refer to carpets with a cut pile. The term is also used to refer to the technique and machines used to produce carpets with a cut pile.
cut loop
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
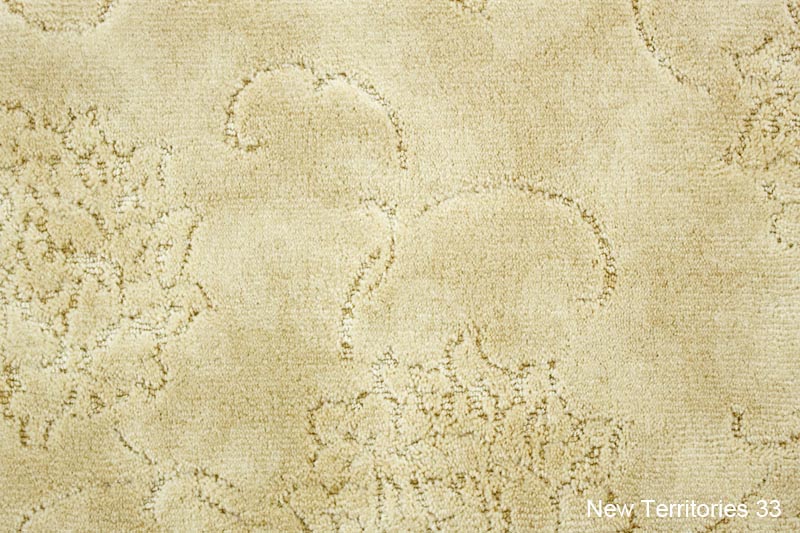


Cut loop carpets are carpets in which both cut piles and loop piles occur in one and the same carpet. It then becomes possible to create both patterns and clear relief structures. Cut loop carpets are soft and comfortable carpets that match many interiors. In most cases the technique does not allow high densities so the carpet is less wear-resistant. Cut loop carpets can conceal soiling quite well. There are different kinds of cut loop carpets: velv-a-loop, standard cut loop and level cut loop.
weaving
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Weaving is a technique to manufacture woven carpet. During the weaving process the pile and the carpet backing are made simultaneously. Weaving carpet is more labour intensive than tufting. Therefore woven carpet is usually more expensive than tufted carpet of comparable quality. There are two main types of woven carpet – Axminster and Wilton. Axminster carpet can be made with unlimited number of colours and is in most of the cases patterned. Wilton carpet can have up to five colours and is in most of the cases plain carpet.
velours (velvet pile carpet)
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń


This is a carpet with a short, dense cut pile. It is a soft and elastic carpet.
With its velvety appearance it has a luxurious and elegant look. It is very suitable for formal spaces.
Velours carpets are sensitive to walking routes and therefore more suitable for spaces with low traffic.
wool
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Wool is a much used natural fibre in the carpet industry. It originates from the fleece of sheep or lambs of the Ovis Aries family. Carpet made with wool has very good appearance retention, good resistance to soiling, low flammability and it is easy to clean too.
tufting
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
Tufting is a technique to manufacture a carpet with a pile where the pile yarn is introduced into a fabric manufactured beforehand then embedded by a coating or adhesive. The pile can be a cut pile or a loop pile or a combination of both.
Wilton
Czytaj więcej
Zwiń
See weaving.